There are thousands upon thousands of jobs available in Connecticut's manufacturing industry. There are currently 411 factories in Connecticut and 159,000 employees. Manufacturing is the biggest contributor to the Gross State Product of Connecticut and provides a high-paying job for its workers. The Connecticut Business and Industry Association recently released a survey of manufacturing workforce needs. They found that 13,000 manufacturing jobs are unfilled in the state, with many companies struggling to hire younger workers.
Connecticut's manufacturing workforce skews older, with one third of the workers being over 55. Many companies moved their manufacturing facilities to reduce labor costs. In turn, other operations adopted new machinery and automation. Although manufacturing used to be considered hazardous and dirty in the past it has gained a better reputation. Nowadays, many companies offer internships and apprenticeships as well as entry-level jobs. Manufacturing is Connecticut’s third largest employment sector. Its high-tech operations are a key competitive advantage.
Connecticut has a number of public and private education programs designed to help people become qualified for manufacturing jobs. The Manufacturing Innovation Fund is a program that supports high schools, universities, vocational high schools, and comprehensive high schools. It supports pre-apprenticeships and online training programs as well as career activities for students in grades K-12.
There are many backgrounds that go into advanced manufacturing. Some are fresh out of highschool, while others have worked for years in a different field before moving to manufacturing. They might have completed a degree at school, or may have joined the workforce after serving in the military. Many companies are willing to pay tuition for advanced manufacturing training programs, and other programs offer wage subsidies for entry level training.
Technical education options are being reintroduced by the state's Comprehensive Schools. One example is the Grasso Tech Welding program. It will begin in fall 2019. Employers that recruit through the EB would be interested in hiring students from Connecticut. The Eastern Connecticut Manufacturing Pipeline, a program that supports advanced manufacturing companies in the area, is available. It is modeled after Eastern Connecticut Workforce Investment Board’s Manufacturing Pipeline.
The Manufacturing Careers Program helps job seekers who are interested to work in manufacturing demonstrate their readiness for entry-level jobs. It connects pre-screened job applicants with manufacturers and other employers. It offers a CNC Basics course that provides industry-integrated career paths. The Advanced Manufacturing Employer Partnership offers wage subsidies to entry-level training for those who enroll in the program.
Young people entering the workforce may not be aware of the manufacturing industry, or may not want to pursue a career in manufacturing. This may make it difficult for them participate in these education programmes. The state has allocated tens of millions of dollars for these programs. These programs are not accessible to young people because they don't know about the existence of these jobs.

One innovative idea for helping address Connecticut's manufacturing jobs shortage is a statewide STEM Town initiative. This would mean reallocating resources, improving education programs and meeting the needs manufacturers.
FAQ
What is the importance of logistics in manufacturing?
Logistics is an integral part of every business. They help you achieve great results by helping you manage all aspects of product flow, from raw materials to finished goods.
Logistics are also important in reducing costs and improving efficiency.
What are manufacturing & logistics?
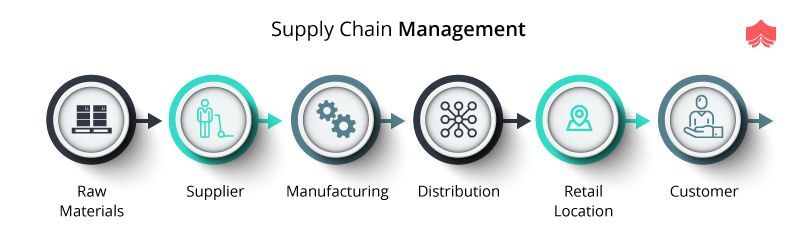
Manufacturing refers to the process of making goods using raw materials and machines. Logistics manages all aspects of the supply chain, including procurement, production planning and distribution, inventory control, transportation, customer service, and transport. Manufacturing and logistics can often be grouped together to describe a larger term that covers both the creation of products, and the delivery of them to customers.
What is meant by manufacturing industries?
Manufacturing Industries are companies that manufacture products. The people who buy these products are called consumers. These companies use various processes such as production, distribution, retailing, management, etc., to fulfill this purpose. They manufacture goods from raw materials using machines and other equipment. This includes all types manufactured goods such as clothing, building materials, furniture, electronics, tools and machinery.
What is the difference between a production planner and a project manager?
The primary difference between a producer planner and a manager of a project is that the manager usually plans and organizes the whole project, while a production planner is only involved in the planning stage.
What are the jobs in logistics?
There are different kinds of jobs available in logistics. Some examples are:
-
Warehouse workers – They load and unload pallets and trucks.
-
Transportation drivers: They drive trucks and trailers and deliver goods and make pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers are people who sort and pack freight into warehouses.
-
Inventory managers - These are responsible for overseeing the stock of goods in warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They organize and plan logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents - They purchase goods and services needed for company operations.
-
Customer service agents - They answer phone calls and respond to emails.
-
Shipping clerks: They process shipping requests and issue bills.
-
Order fillers: They fill orders based off what has been ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors - They check incoming and outgoing products for defects.
-
Other - Logistics has many other job opportunities, including transportation supervisors, logistics specialists, and cargo specialists.
What are the responsibilities for a manufacturing manager
A manufacturing manager has to ensure that all manufacturing processes work efficiently and effectively. They should also be aware of any problems within the company and act accordingly.
They must also be able to communicate with sales and marketing departments.
They should also be aware of the latest trends in their industry and be able to use this information to help improve productivity and efficiency.
Statistics
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma is defined as "the application of statistical process control (SPC) techniques to achieve continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department developed it at their Tokyo plant in Japan in 1986. Six Sigma's core idea is to improve the quality of processes by standardizing and eliminating defects. Many companies have adopted this method in recent years. They believe there is no such thing a perfect product or service. Six Sigma seeks to reduce variation between the mean production value. This means that you can take a sample from your product and then compare its performance to the average to find out how often the process differs from the norm. If the deviation is excessive, it's likely that something needs to be fixed.
Understanding the nature of variability in your business is the first step to Six Sigma. Once you have a good understanding of the basics, you can identify potential sources of variation. You'll also want to determine whether these variations are random or systematic. Random variations occur when people do mistakes. Symmetrical variations are caused due to factors beyond the process. Random variations would include, for example, the failure of some widgets to fall from the assembly line. It would be considered a systematic problem if every widget that you build falls apart at the same location each time.
Once you've identified the problem areas you need to find solutions. It might mean changing the way you do business or redesigning it entirely. To verify that the changes have worked, you need to test them again. If they didn't work, then you'll need to go back to the drawing board and come up with another plan.