During the period of analysis, Mexico was one of the three main actors in the DVA trade network for global manufacturing exports. The automotive industry has not been as successful as the textiles sector. Both industries are still considered important in Mexico's export markets and relevant for job creation.
The Mexican auto industry is one the largest suppliers of American parts. It is also one among the fastest-growing industries in Mexico. It has not been able drag the rest of the country onto a high growth path. The industry's transition from a domestic-oriented one to a regional automotive parts/automobile chain is happening. This transition is being driven by both regional processes as well as foreign direct investment.
Mexico has many programs that have helped the automotive industry. It has achieved remarkable penetration in global markets and has emerged as the U.S.'s largest supplier for auto parts. It has also been able to benefit from foreign direct investments, which have been key factors in increasing its global role in value chains.
The Mexican automotive industry plays a significant role in both the GVCs in Europe and the United States. Mexico's economy has relied heavily on the automotive industry since the 1970s. But it has not had the same penetration into the world market as textiles. In addition, it has not achieved a high level of expansion in its output, although it has achieved remarkable penetration into the world market.
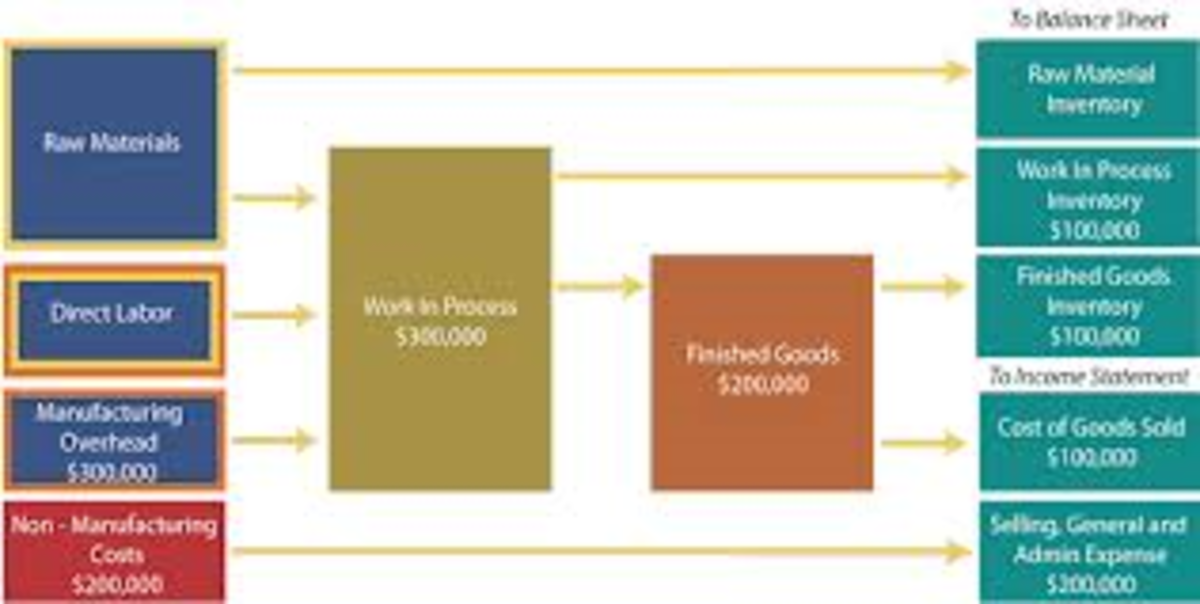
To analyze the relationship between international trade, labour and the Mexican manufacturing sector, the study employs the framework of decent-work indicators (ILO). Indicators are based on official data and taken into account the links between trade agreements and labour regulations in Mexico. Input-output analysis is part of the international trade indicators. It shows that Mexico plays an insignificant role in the global value-added to manufacturing exports.

The study also examines how trade liberalization affects employment in Mexico's manufacturing industry. It uses the System of National Accounts to build a set of indicators for decent work in two industrial areas of Mexico. These indicators are compiled into a time series and used to analyze the Mexican evolution of decent employment. The study finds that the level of D V A G V C in the manufacturing sector is considerably lower than in the textile sector. The study also shows that the level and employment in the automotive sector is lower than in the textile industry. In addition, the study finds that the level of real wages has declined since the beginning of the analysis. The nominal wage adjustment did not compensate for the decline in real wages. The study finds that the level of DVA in transport equipment exports has increased in the past decade, while the level of DVA in textile exports has decreased.
FAQ
What are manufacturing & logistics?
Manufacturing is the production of goods using raw materials. Logistics is the management of all aspects of supply chain activities, including procurement, production planning, distribution, warehousing, inventory control, transportation, and customer service. As a broad term, manufacturing and logistics often refer to both the creation and delivery of products.
What is the distinction between Production Planning or Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. Forecasting and identifying production capacity are two key elements to this process.
Scheduling is the process that assigns dates to tasks so they can get completed within a given timeframe.
What skills is required for a production planner?
Production planners must be flexible, organized, and able handle multiple tasks. You must also be able to communicate effectively with clients and colleagues.
How can efficiency in manufacturing be improved?
First, identify the factors that affect production time. Next, we must find ways to improve those factors. If you don't know where to start, then think about which factor(s) have the biggest impact on production time. Once you have identified them, it is time to identify solutions.
Statistics
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
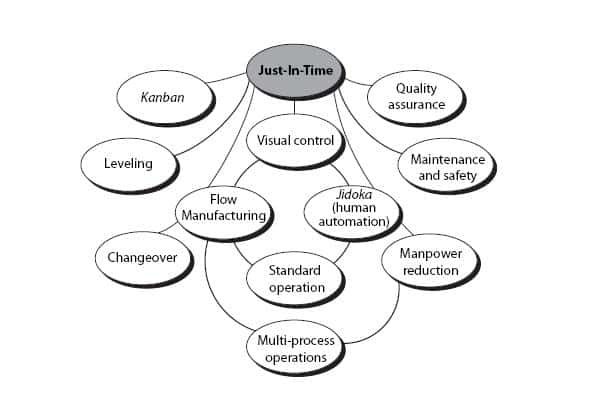
How to Use Just-In-Time Production
Just-in-time (JIT) is a method that is used to reduce costs and maximize efficiency in business processes. It is a process where you get the right amount of resources at the right moment when they are needed. This means that you only pay the amount you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. He observed how workers were paid overtime if there were delays in their work. He decided to ensure workers have enough time to do their jobs before starting work to improve productivity.
JIT is an acronym that means you need to plan ahead so you don’t waste your money. The entire project should be looked at from start to finish. You need to ensure you have enough resources to tackle any issues that might arise. If you anticipate that there might be problems, you'll have enough people and equipment to fix them. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are many types of JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will allow you to track how much material you have left over after using it. This will allow you to calculate how long it will take to make more.
-
Inventory-based : You can stock the materials you need in advance. This allows you to forecast how much you will sell.
-
Project-driven: This approach involves setting aside sufficient funds to cover your project's costs. When you know how much you need, you'll purchase the appropriate amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT: This is the most popular form of JIT. You allocate resources based on the demand. You might assign more people to help with orders if there are many. If you don't have many orders, you'll assign fewer people to handle the workload.
-
Cost-based : This is similar in concept to resource-based. But here, you aren't concerned about how many people your company has but how much each individual costs.
-
Price-based: This approach is very similar to the cost-based method except that you don't look at individual workers costs but the total cost of the company.
-
Material-based: This is quite similar to cost-based, but instead of looking at the total cost of the company, you're concerned with how much raw materials you spend on average.
-
Time-based JIT: A variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each employee, you will focus on the time it takes to complete a project.
-
Quality-based JIT: This is another variation of resource based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each worker or how long it takes, think about how high quality your product is.
-
Value-based JIT: This is the latest form of JIT. You don't worry about whether the products work or if they meet customer expectations. Instead, you are focused on adding value to the marketplace.
-
Stock-based is an inventory-based system that measures the number of items produced at any given moment. This is used to increase production and minimize inventory.
-
Just-intime (JIT), planning is a combination JIT management and supply chain management. It is the process that schedules the delivery of components within a short time of their order. This is important as it reduces lead time and increases throughput.