
The machines that machine operators use to make repairs are a wide range of machines. These machines perform repairs on metal products such a car. They can also form new alloys and precision metal parts. Machine operators are frequently exposed to toxic chemicals. A good machinist is detail-oriented, has strong communication skills, and is able to interpret mechanical blueprints.
Machinists can work part-time or full-time. Many of these machinists begin work right out high school. However, some machinists complete an apprenticeship before moving up to a full-time position. Others may pursue associate degrees. Some machinists might even choose to pursue engineering or computer-aided designing (CAD) degrees.
Machinists often work in factories or specialty shops. Although these positions are noisy and can expose you to potentially dangerous materials, they offer great opportunities for problem solving. Machines used by machinists can be manual or automatic. Those with a lot of experience in the field can move up to supervisory or managerial positions. The need for machinists is increasing as baby boomers retire. As machine shops modernize for automation, job security increases.
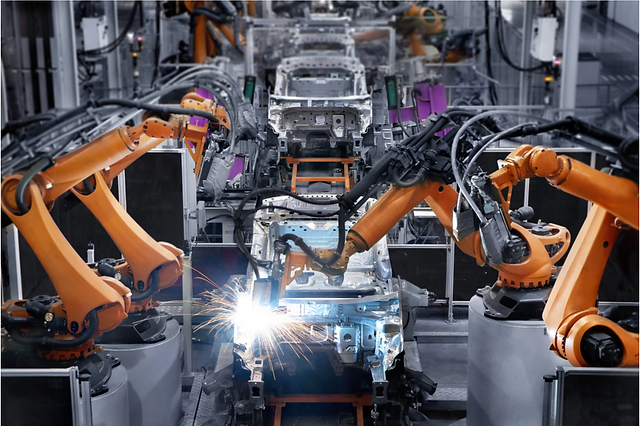
Depending on their employer, machinists could be assigned specific tasks such as setting up machines, fixing them, or making sure the parts they produce are compliant with quality standards. They can also operate assembly lines, which are machines that are controlled by either a human or robot. Other responsibilities include programming the machines and monitoring them, and reading blueprints.
Machinists work in a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum brass, copper, and others. While most machinists work with machines that make metal parts, it is not uncommon for them to be required to work with other materials.
Generally, machinists have a high school diploma, although some employers may require an associate's degree. If you are interested in becoming a machinist, you can start with a training program that can last up to four years. To get more experience and learn, you can work alongside a mentor at work. Be sure to ask your mentor about other opportunities for training, such as apprenticeships or additional education.
Regardless of the company, machinists must work with others. They can either work as part of a larger team or individually, but they must always follow safety procedures. You should always wear proper safety equipment such as gloves, earplugs, and masks. Machinists may also be exposed to chemicals, fumes, or other environmental hazards. Fortunately, machinists do not have to be under constant time pressure.
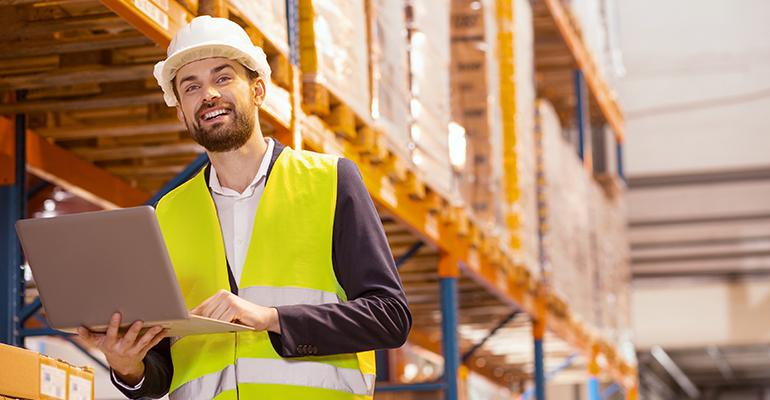

In addition to on-the job training, machinists have the option of enrolling in college courses and joining trade unions. Machinists with union membership enjoy better benefits and greater job security. Union members have access to health insurance and retirement plans. Many colleges offer 2-year programs for machining associates.
A degree in machinist will allow you to climb the corporate ladder. Machine operators will become more in demand as the demand for parts for cars increases. Job growth is projected to be 7% between 2020 and 2030. In the coming decades, machinists will remain in high demand due to increased use of artificial Intelligence and retooling of automation.
FAQ
What are the 7 Rs of logistics?
The 7R's of Logistics is an acronym for the seven basic principles of logistics management. It was developed by International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL), and published as part of their "Seven Principles of Logistics Management Series" in 2004.
The acronym is composed of the following letters.
-
Responsible – ensure that all actions are legal and don't cause harm to anyone else.
-
Reliable: Have faith in your ability or the ability to honor any promises made.
-
It is reasonable to use resources efficiently and not waste them.
-
Realistic - Take into consideration all aspects of operations including cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and other factors.
-
Respectful: Treat others with fairness and equity
-
You are resourceful and look for ways to save money while increasing productivity.
-
Recognizable is a company that provides customers with value-added solutions.
What does it take for a logistics enterprise to succeed?
To be a successful businessman in logistics, you will need many skills and knowledge. Good communication skills are essential to effectively communicate with your suppliers and clients. You must be able analyze data and draw out conclusions. You need to be able work under pressure and manage stressful situations. To improve efficiency, you must be innovative and creative. You will need strong leadership skills to motivate and direct your team members towards achieving their organizational goals.
You must be organized to meet tight deadlines.
Why automate your warehouse?
Modern warehousing has seen automation take center stage. Increased demand for efficient and faster delivery has resulted in a rise in e-commerce.
Warehouses need to adapt quickly to meet changing needs. Technology investment is necessary to enable warehouses to respond quickly to changing demands. Automation of warehouses offers many benefits. Here are some of the reasons automation is worth your investment:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Safety enhancements
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies to scale more easily
-
It makes workers more efficient
-
It gives visibility to everything that happens inside the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
This reduces downtime while increasing uptime
-
You can be sure that high-quality products will arrive on time
-
Eliminates human error
-
It helps ensure compliance with regulations
What is production planning?
Production Planning includes planning for all aspects related to production. This document will ensure everything is in order and ready to go when you need it. It should also provide information about how best to produce the best results while on set. This includes information on shooting times, locations, cast lists and crew details.
The first step in filming is to define what you want. You may have decided where to shoot or even specific locations you want to use. Once you've identified the locations and scenes you want to use, you can begin to plan what elements you need for each scene. For example, you might decide that you need a car but don't know exactly what model you want. In this case, you could start looking up cars online to find out what models are available and then narrow your choices by choosing between different makes and models.
After you've found the perfect car, it's time to start thinking about adding extras. Do you need people sitting in the front seats? You might also need someone to help you get around the back. Maybe you want to change the interior color from black to white? These questions can help you decide the right look for your car. You can also think about the type of shots you want to get. You will be filming close-ups and wide angles. Maybe the engine or steering wheel is what you are looking to film. These factors will help you determine which car style you want to film.
Once you have all the information, you are ready to create a plan. A schedule will tell you when you need to start shooting and when you need to finish. You will need to know when you have to be there, what time you have to leave and when your return home. This way, everyone knows what they need to do and when. You can also make sure to book extra staff in advance if you have to hire them. It is not worth hiring someone who won’t show up because you didn’t tell him.
Also, consider how many days you will be filming your schedule. Some projects are quick and easy, while others take weeks. While creating your schedule, it is important to remember whether you will require more than one shot per day. Multiplying takes in the same area will result both in increased costs and a longer time. It is better to be cautious and take fewer shots than you risk losing money if you are not sure if multiple takes are necessary.
Budgeting is another important aspect of production planning. You will be able to manage your resources if you have a realistic budget. If you have to reduce your budget due to unexpected circumstances, you can always lower it later. However, it is important not to overestimate the amount that you will spend. If you underestimate how much something costs, you'll have less money to pay for other items.
Production planning can be a complex process. However, once you know how everything works together it will become easier to plan future projects.
What are the four types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process that transforms raw materials into useful products. It includes many different activities like designing, building and testing, packaging, shipping and selling, as well as servicing.
How can overproduction in manufacturing be reduced?
In order to reduce excess production, you need to develop better inventory management methods. This would reduce the time spent on unproductive activities like purchasing, storing and maintaining excess stock. This could help us free up our time for other productive tasks.
This can be done by using a Kanban system. A Kanban board is a visual display used to track work in progress. A Kanban system allows work items to move through several states before reaching their final destination. Each state represents a different priority level.
If work is moving from one stage to the other, then the current task can be completed and moved on to the next. But if a task remains in the beginning stages it will stay that way until it reaches its end.
This allows for work to continue moving forward, while also ensuring that there is no work left behind. Managers can see how much work has been done and the status of each task at any time with a Kanban Board. This information allows managers to adjust their workflow based off real-time data.
Lean manufacturing is another way to manage inventory levels. Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste in all phases of production. Any product that isn't adding value can be considered waste. Here are some examples of common types.
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Packaging that is not necessary
-
Materials in excess
Manufacturers can reduce their costs and improve their efficiency by using these ideas.
Statistics
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use Just-In-Time Production
Just-intime (JIT), a method used to lower costs and improve efficiency in business processes, is called just-in-time. It's a way to ensure that you get the right resources at just the right time. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor was the first to coin this term. He developed it while working as a foreman during the early 1900s. Taylor observed that overtime was paid to workers if they were late in working. He decided that workers would be more productive if they had enough time to complete their work before they started to work.
JIT teaches you to plan ahead and prepare everything so you don’t waste time. You should also look at the entire project from start to finish and make sure that you have sufficient resources available to deal with any problems that arise during the course of your project. You will have the resources and people to solve any problems you anticipate. This way you won't be spending more on things that aren’t really needed.
There are many types of JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven JIT: You order the parts and materials you need for your project every other day. This will let you track the amount of material left over after you've used it. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This allows you to store the materials necessary for your projects in advance. This allows one to predict how much they will sell.
-
Project-driven: This means that you have enough money to pay for your project. You will be able to purchase the right amount of materials if you know what you need.
-
Resource-based JIT: This type of JIT is most commonly used. Here you can allocate certain resources based purely on demand. You might assign more people to help with orders if there are many. You'll have fewer orders if you have fewer.
-
Cost-based : This is similar in concept to resource-based. But here, you aren't concerned about how many people your company has but how much each individual costs.
-
Price-based: This is a variant of cost-based. However, instead of focusing on the individual workers' costs, this looks at the total price of the company.
-
Material-based is an alternative to cost-based. Instead of looking at the total cost in the company, this method focuses on the average amount of raw materials that you consume.
-
Time-based JIT is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of looking at the labor costs and time it takes to make a product, think about its quality.
-
Value-based JIT : This is the newest type of JIT. In this scenario, you're not concerned about how products perform or whether customers expect them to meet their expectations. Instead, you focus on the added value that you provide to your market.
-
Stock-based: This is an inventory-based method that focuses on the actual number of items being produced at any given time. It's useful when you want maximum production and minimal inventory.
-
Just-in time (JIT), planning: This is a combination JIT/supply chain management. It is the process that schedules the delivery of components within a short time of their order. It's important because it reduces lead times and increases throughput.