
What are the factors that are responsible for rapid advancement in our society? Science or Technology? Technology? Innovation? Ingenuity? Or perhaps something else altogether? Here are 10 examples to help you understand how to write a sentence. The lessons can be downloaded and you can practice them as often as you wish. This will make it easy to use the lessons in everyday conversation. Below are ten examples that demonstrate rapid advancement.
Science
Science has made huge strides in the last century. It is no secret. The invention the elevator launched a new wave and introduced the age to skyscrapers. MULTI, a horizontal elevator, is in development, which opens up new opportunities for urban design and building. The Human Genome Project identified every gene in human DNA. This opened up new possibilities for medical research as well as the creation of new biotech companies.
Technology
Technology has impacted every aspect of our everyday lives. This revolution has impacted every sector of society over the past 50 years. Individuals and businesses alike will feel the impact of new innovations on their daily lives. These are some of the ways technology can help you use your advantage. These trends can be used to enhance your business. Continue reading for more information. Don't forget about asking yourself if you are ready to keep up with the times.
Innovation
Technological innovations have been a key factor in the development of industrial nations throughout history. The development of new technology has led governments to shift their focus away from science-technology policies and towards research and innovation policies. This shift has allowed for the creation of new models of innovation that take into account many external factors. Technology innovation includes social capital, in addition to firm factors. Changing social capital results in changes in innovation patterns, which differ between national systems.
Ingenuity
Despite the rapid growth in our society, a lack of ingenuity can slow progress. Rapid development depends on the availability new technologies and ideas. The availability of these resources is an important determinant of society's adaptability. Some poor societies will experience a widening gap between the supply and demand of ingenuity, which will be subject to the stresses created by scarcity. A chronic shortage ingenuity could lead to civil unrest and social decay.
Machine learning
Modern computer hardware and software has made it possible for larger models to be trained faster. The use of graphics processing units, originally designed for video games, for data crunching is a great example. These units can crunch data much faster than traditional processor chips. Tensor units are another silicon-level advancement. Cloud computing has made machine learning applications scaleable. Cloud computing is easy to use and has many applications.

Scientific ingenuity
The bicycle race analogy is a great example of the relationship between scientific ingenuity, scientific progress and scientific creativity. In this example, scientists and researchers progress together over a longer period of time. Only a handful of individuals are able to break away and win. While scientific ingenuity is nearly limitless, we cannot keep up with the demands placed on it. This is because the delivery of ingenuity is slowing down the pace of progress.
FAQ
What skills do production planners need?
Production planners must be flexible, organized, and able handle multiple tasks. You must also be able to communicate effectively with clients and colleagues.
What is the role of a manager in manufacturing?
A manufacturing manager has to ensure that all manufacturing processes work efficiently and effectively. They should be aware of any issues within the company and respond accordingly.
They should also be able communicate with other departments, such as sales or marketing.
They should be up to date on the latest trends and be able apply this knowledge to increase productivity and efficiency.
How does manufacturing avoid bottlenecks in production?
The key to avoiding bottlenecks in production is to keep all processes running smoothly throughout the entire production cycle, from the time you receive an order until the time when the product ships.
This includes both planning for capacity and quality control.
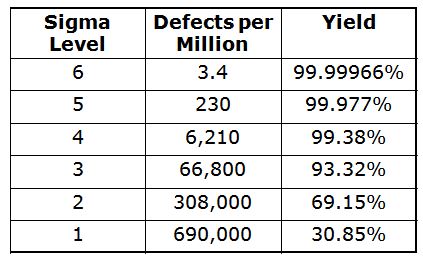
This can be done by using continuous improvement techniques, such as Six Sigma.
Six Sigma management is a system that improves quality and reduces waste within your organization.
It emphasizes consistency and eliminating variance in your work.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics?
The acronym "7R's" of Logistics stands for seven principles that underpin logistics management. It was developed and published by the International Association of Business Logisticians in 2004 as part of the "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The acronym is composed of the following letters.
-
Responsible - ensure that actions are in compliance with legal requirements and do not cause harm to others.
-
Reliable - You can have confidence that you will fulfill your promises.
-
Reasonable - make sure you use your resources well and don't waste them.
-
Realistic - Take into consideration all aspects of operations including cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and other factors.
-
Respectful - Treat people fairly and equitably
-
Be resourceful: Look for opportunities to save money or increase productivity.
-
Recognizable: Provide customers with value-added service
Statistics
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just In Time Method in Production
Just-intime (JIT), a method used to lower costs and improve efficiency in business processes, is called just-in-time. This is where you have the right resources at the right time. This means that you only pay for what you actually use. Frederick Taylor, a 1900s foreman, first coined the term. After observing how workers were paid overtime for late work, he realized that overtime was a common practice. He decided to ensure workers have enough time to do their jobs before starting work to improve productivity.
The idea behind JIT is that you should plan ahead and have everything ready so you don't waste money. Also, you should look at the whole project from start-to-finish and make sure you have the resources necessary to address any issues. You will have the resources and people to solve any problems you anticipate. This way you won't be spending more on things that aren’t really needed.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This type of JIT allows you to order the parts/materials required for your project on a regular basis. This will allow you to track how much material you have left over after using it. This will let you know how long it will be to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This allows you to store the materials necessary for your projects in advance. This allows you to predict how much you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This method allows you to set aside enough funds for your project. You will be able to purchase the right amount of materials if you know what you need.
-
Resource-based JIT: This is the most popular form of JIT. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. For example, if there is a lot of work coming in, you will have more people assigned to them. If there aren't many orders, you will assign fewer people.
-
Cost-based: This is the same as resource-based except that you don't care how many people there are but how much each one of them costs.
-
Price-based: This approach is very similar to the cost-based method except that you don't look at individual workers costs but the total cost of the company.
-
Material-based: This approach is similar to cost-based. However, instead of looking at the total cost for the company, you look at how much you spend on average on raw materials.
-
Time-based: Another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of worrying about how much each worker costs, you can focus on how long the project takes.
-
Quality-based JIT is another variant of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each worker or how long it takes, think about how high quality your product is.
-
Value-based JIT : This is the newest type of JIT. In this scenario, you're not concerned about how products perform or whether customers expect them to meet their expectations. Instead, your goal is to add value to the market.
-
Stock-based. This method is inventory-based and focuses only on the actual production at any given point. This method is useful when you want to increase production while decreasing inventory.
-
Just-in time (JIT), planning: This is a combination JIT/supply chain management. It's the process of scheduling delivery of components immediately after they are ordered. This is important as it reduces lead time and increases throughput.