
Cybersecurity is crucial for manufacturers as the Internet of Things (IoT), transforms the manufacturing sector. Companies must ensure that their customer information and assets are protected in light of the increasing number of cyberattacks. Using the right technology can help companies respond to threats and stay secure. You can ensure the safety and security of your industrial equipment with physical security systems that include cameras, locks, access cards, and cameras.
Kaspersky Labs reports that one third of all cybersecurity incidents target manufacturers. These threats are becoming more complicated and prevalent. These can include malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks. Manufacturers need to protect their intellectual property, designs and products. It is important to develop a strategy to help mitigate cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity is essential for protecting data and information of manufacturers such as customer order details, product specifications, and design plans. The plan should also include how to react to a possible cyber attack. This can run between $3 to $6 million. Companies are vulnerable to theft of intellectual property, data breaches, and disruption of production lines. Many manufacturers find it difficult to keep up with cyberattacks.
Security for manufacturers is crucial to protect employee and customer data as well the company’s reputation and revenue. To ensure that your cybersecurity plan is successful, it's important to conduct a thorough audit of your systems to identify vulnerabilities and determine your overall readiness.
If you're ready to get started, contact your local Manufacturing Executive Program (MEP) center for resources and advice. You'll receive expert advice on how to make your business safer from cyberattacks.
Aside from performing an audit of the systems, it is important to establish a backup plan. It's also crucial to test your system regularly to ensure it works as intended. This will help reduce the risk of an attack.
Many manufacturers aren't using cybersecurity measures, such as data standards. Nearly half of OEMs use outdated or non-compliant software and hardware. However, more companies are investing in digital tech. The industry is being transformed by data-related technologies such as cloud computing, sensors, networked machines and sensor networks. The increased globalization of the industry and the Internet of Things (IoT), have raised new concerns. However, a cybersecurity strategy can help ensure your organization is safe.
It's crucial to understand the different requirements of different manufacturing industries before developing a cybersecurity plan. For example, global companies with long supply chains have to comply with standards that are specific to their country, region, and partner. On the other hand, manufacturers that are small or medium-sized often have less stringent cybersecurity policies. No matter your company size, it is important to have a comprehensive plan in place to protect your business against cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity Framework for Manufacturers is a resource that helps manufacturers to protect their business from cyberattacks. It's available from the National Institute of Standards and Technology. This framework provides a plan for managing cybersecurity activities within a variety sectors, including industrial manufacture.
FAQ
How can we reduce manufacturing overproduction?
The key to reducing overproduction lies in developing better ways to manage inventory. This would reduce the time needed to manage inventory. This could help us free up our time for other productive tasks.
One way to do this is to adopt a Kanban system. A Kanbanboard is a visual tool that allows you to keep track of the work being done. In a Kanban system, work items move through a sequence of states until they reach their final destination. Each state is assigned a different priority.
For instance, when work moves from one stage to another, the current task is complete enough to be moved to the next stage. But if a task remains in the beginning stages it will stay that way until it reaches its end.
This keeps work moving and ensures no work is lost. A Kanban board allows managers to monitor how much work is being completed at any given moment. This allows them the ability to adjust their workflow using real-time data.
Lean manufacturing, another method to control inventory levels, is also an option. Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste in all phases of production. Anything that doesn't add value to the product is considered waste. The following are examples of common waste types:
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Overstock materials
Manufacturers can reduce their costs and improve their efficiency by using these ideas.
What skills should a production planner have?
You must be flexible and organized to become a productive production planner. Effective communication with clients and colleagues is essential.
What kind of jobs are there in logistics?
Logistics can offer many different jobs. Some examples are:
-
Warehouse workers – They load and unload pallets and trucks.
-
Transportation drivers – They drive trucks or trailers to transport goods and perform pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers – They sort and package freight at warehouses.
-
Inventory managers - They oversee the inventory of goods in warehouses.
-
Sales representatives: They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators – They plan and coordinate logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents: They are responsible for purchasing goods and services to support company operations.
-
Customer service representatives are available to answer customer calls and emails.
-
Shipping clerks – They process shipping orders, and issue bills.
-
Order fillers: They fill orders based off what has been ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors (QCI) - They inspect all incoming and departing products for potential defects.
-
Others - There are many other types of jobs available in logistics, such as transportation supervisors, cargo specialists, etc.
What is the responsibility of a manufacturing manager?
A manufacturing manager has to ensure that all manufacturing processes work efficiently and effectively. They should also be aware of any problems within the company and act accordingly.
They should also be able and comfortable communicating with other departments like sales and marketing.
They should be informed about industry trends and be able make use of this information to improve their productivity and efficiency.
Is it necessary to be familiar with Manufacturing Processes before we learn about Logistics.
No. No. Understanding the manufacturing process will allow you to better understand logistics.
Why automate your factory?
Modern warehousing has seen automation take center stage. With the rise of ecommerce, there is a greater demand for faster delivery times as well as more efficient processes.
Warehouses should be able adapt quickly to new needs. Technology investment is necessary to enable warehouses to respond quickly to changing demands. The benefits of automating warehouses are numerous. Here are some reasons why it's worth investing in automation:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Improves accuracy
-
Safety increases
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale up more easily
-
It makes workers more efficient
-
The warehouse can be viewed from all angles.
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reducing downtime and increasing uptime
-
High quality products delivered on-time
-
Eliminates human error
-
Assure compliance with regulations
Statistics
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
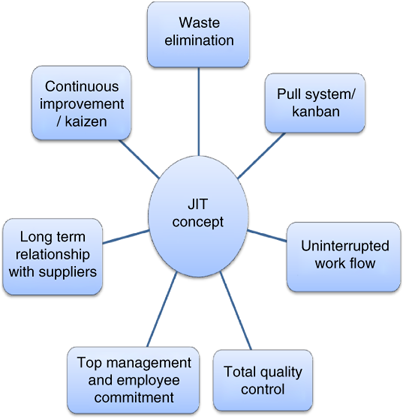
How to Use Just-In-Time Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It's the process of obtaining the right amount and timing of resources when you need them. This means that only what you use is charged to your account. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. He saw how overtime was paid to workers for work that was delayed. He decided to ensure workers have enough time to do their jobs before starting work to improve productivity.
JIT teaches you to plan ahead and prepare everything so you don’t waste time. Look at your entire project, from start to end. Make sure you have enough resources in place to deal with any unexpected problems. If you anticipate that there might be problems, you'll have enough people and equipment to fix them. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This type of JIT allows you to order the parts/materials required for your project on a regular basis. This will let you track the amount of material left over after you've used it. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This is a type where you stock the materials required for your projects in advance. This allows for you to anticipate how much you can sell.
-
Project-driven: This is an approach where you set aside enough funds to cover the cost of your project. You will be able to purchase the right amount of materials if you know what you need.
-
Resource-based JIT: This type of JIT is most commonly used. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. For example, if there is a lot of work coming in, you will have more people assigned to them. If you don't receive many orders, then you'll assign fewer employees to handle the load.
-
Cost-based: This is the same as resource-based except that you don't care how many people there are but how much each one of them costs.
-
Price-based: This is a variant of cost-based. However, instead of focusing on the individual workers' costs, this looks at the total price of the company.
-
Material-based: This is very similar to cost-based but instead of looking at total costs of the company you are concerned with how many raw materials you use on an average.
-
Time-based: Another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based: This is yet another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about how much each employee costs or how long it takes to manufacture something, you think about how good the quality of your product is.
-
Value-based: This is one of the newest forms of JIT. You don't worry about whether the products work or if they meet customer expectations. Instead, you focus on the added value that you provide to your market.
-
Stock-based is an inventory-based system that measures the number of items produced at any given moment. It's useful when you want maximum production and minimal inventory.
-
Just-intime (JIT), planning is a combination JIT management and supply chain management. This refers to the scheduling of the delivery of components as soon after they are ordered. It's important as it reduces leadtimes and increases throughput.