
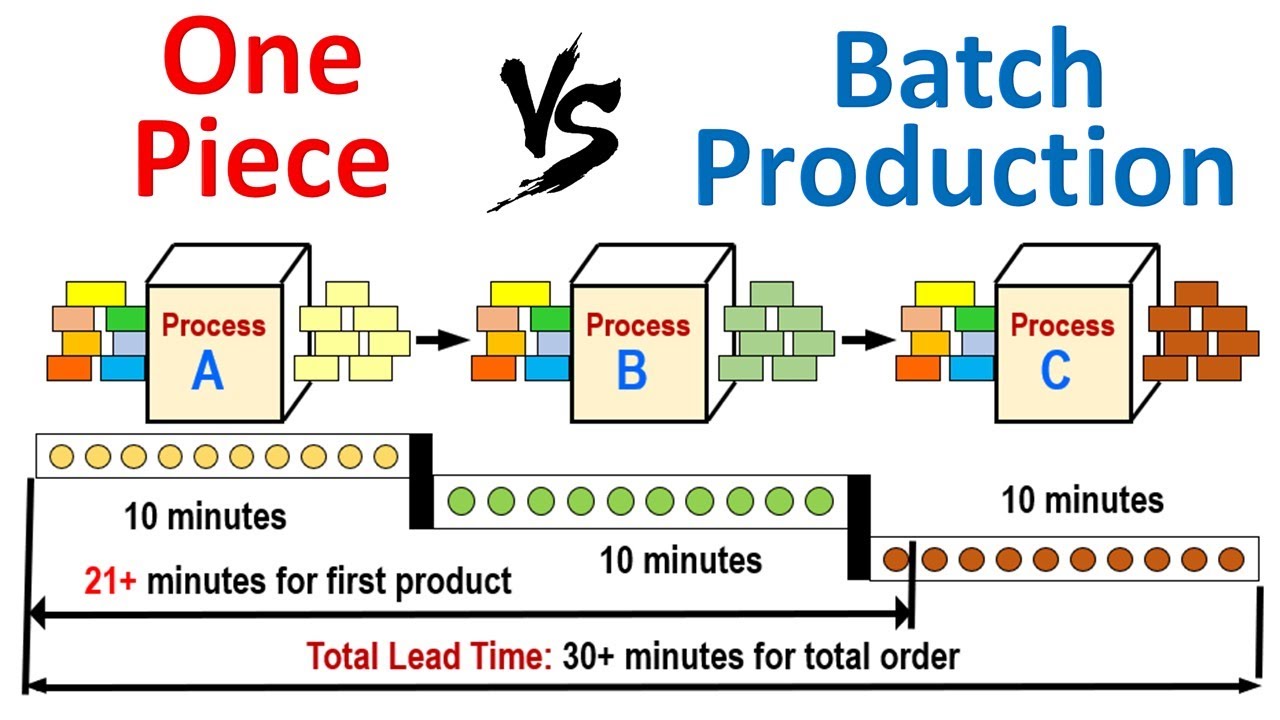
The production method of time manufacturing is one that has a constant flow of products throughout the supply chain. It is an effective and efficient method of manufacturing goods, and avoiding overproduction.
Just in time production
Toyota Production System is a method of manufacturing that utilizes Just in Time Production. This allows companies to ship parts and materials directly to the plant so that they will be available when needed.
Businesses can also reduce their inventory costs and save on storage space. This allows a company to produce less product while having more money to spend on other areas.
The automobile industry is a good example of just-in-time production. The automobile industry is a good example of just-in-time production. They instead wait for orders and keep as few inventory as possible.

The PPS system allows them to see which parts are in stock and which have been ordered. Then, they can plan production accordingly.
Suppliers can provide raw materials to reduce production costs and guarantee high-quality components.
They can use a purchase order to specify when the parts should arrive at their facility. The supplier then delivers the parts to the company and they begin building the car.
The car can be completed and delivered in a timely way by the company. The company can provide a consistent and reliable product to its customers.
Just-in time production is often used by small companies who need to create products but do not have a large inventory or complex supply chains. They can build strong relationships to minimize stockouts, shortages or other risks.
Using the Just in Time method is beneficial to manufacturing firms located near a big city, or who have suppliers close by that can quickly and easily provide parts. It can improve employee retention if employees stay at the same firm for a longer period.
Just-in-time delivery is a method of supply chain management based on the idea that a product should arrive at an address and be ready to be shipped as soon as it is required by the client. This is a crucial delivery for businesses with an ecommerce presence as well as customers who require their products to be delivered as quickly as they can.
Just in time delivery is popular because it allows retailers and customers to choose from more convenient and quicker shipping options. Customers are able to select the most convenient and fast shipping method for their order.
Businesses can also use just-in-time delivery to respond to supply chain failures, such as those that occur due to unforeseen delays and accidents. It can help businesses stay competitive and in business.
FAQ
What is the role of a production manager?
A production planner makes sure all project elements are delivered on schedule, within budget, as well as within the agreed scope. They ensure that the product or service is of high quality and meets client requirements.
What is the best way to learn about manufacturing?
Experience is the best way for you to learn about manufacturing. You can read books, or watch instructional videos if you don't have the opportunity to do so.
What types of jobs can you find in logistics
There are different kinds of jobs available in logistics. Some examples are:
-
Warehouse workers – They load and unload pallets and trucks.
-
Transport drivers - These are people who drive trucks and trailers to transport goods or perform pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers: They sort and package freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers – These people oversee inventory at warehouses.
-
Sales representatives: They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents are those who purchase goods and services for the company.
-
Customer service agents - They answer phone calls and respond to emails.
-
Ship clerks - They issue bills and process shipping orders.
-
Order fillers - They fill orders based on what is ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors – They inspect incoming and outgoing products to ensure that there are no defects.
-
Others – There are many other types available in logistics. They include transport supervisors, cargo specialists and others.
What is the job of a manufacturer manager?
A manufacturing manager has to ensure that all manufacturing processes work efficiently and effectively. They should be alert for any potential problems in the company and react accordingly.
They should also be able and comfortable communicating with other departments like sales and marketing.
They must also keep up-to-date with the latest trends in their field and be able use this information to improve productivity and efficiency.
How can excess manufacturing production be reduced?
It is essential to find better ways to manage inventory to reduce overproduction. This would reduce time spent on activities such as purchasing, stocking, and maintaining excess stock. This will allow us to free up resources for more productive tasks.
This can be done by using a Kanban system. A Kanban board can be used to monitor work progress. In a Kanban system, work items move through a sequence of states until they reach their final destination. Each state represents a different priority level.
When work is completed, it can be transferred to the next stage. It is possible to keep a task in the beginning stages until it gets to the end.
This helps to keep work moving forward while ensuring that no work is left behind. Managers can see how much work has been done and the status of each task at any time with a Kanban Board. This information allows them to adjust their workflow based on real-time data.
Lean manufacturing is another way to manage inventory levels. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste throughout the entire production chain. Any product that isn't adding value can be considered waste. Here are some examples of common types.
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Materials in excess
These ideas can help manufacturers improve efficiency and reduce costs.
What does it mean to be a manufacturer?
Manufacturing Industries is a group of businesses that produce goods for sale. Consumers are those who purchase these products. To accomplish this goal, these companies employ a range of processes including distribution, sales, management, and production. They manufacture goods from raw materials using machines and other equipment. This includes all types and varieties of manufactured goods, such as food items, clothings, building supplies, furnitures, toys, electronics tools, machinery vehicles, pharmaceuticals medical devices, chemicals, among others.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma is "the application statistical process control (SPC), techniques for continuous improvement." It was developed by Motorola's Quality Improvement Department at their plant in Tokyo, Japan, in 1986. The basic idea behind Six Sigma is to improve quality by improving processes through standardization and eliminating defects. Since there are no perfect products, or services, this approach has been adopted by many companies over the years. Six Sigma seeks to reduce variation between the mean production value. It is possible to measure the performance of your product against an average and find the percentage of time that it differs from the norm. If you notice a large deviation, then it is time to fix it.
Understanding the dynamics of variability within your business is the first step in Six Sigma. Once you've understood that, you'll want to identify sources of variation. It is important to identify whether the variations are random or systemic. Random variations happen when people make errors; systematic variations are caused externally. Random variations would include, for example, the failure of some widgets to fall from the assembly line. But if you notice that every widget you make falls apart at the exact same place each time, this would indicate that there is a problem.
Once you've identified where the problems lie, you'll want to design solutions to eliminate those problems. That solution might involve changing the way you do things or redesigning the process altogether. You should then test the changes again after they have been implemented. If they don’t work, you’ll need to go back and rework the plan.