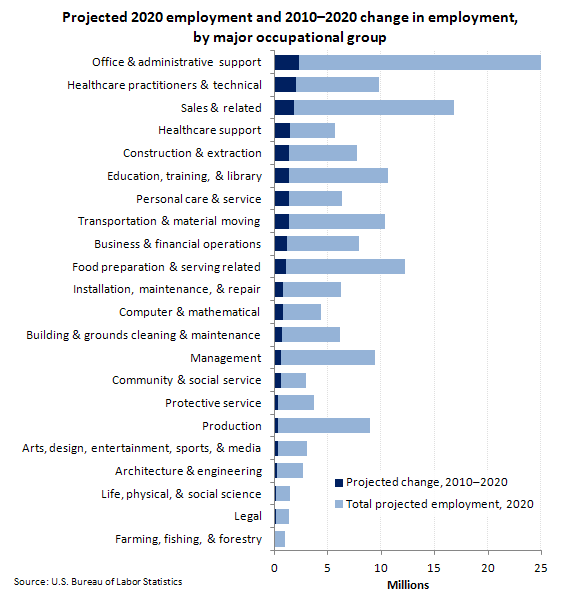
Six-Sigma, lean and Lean are complementary methods of improving processes. Both tools can be used to solve problems but each approach has its own strengths. Six-Sigma, a statistical process control technique that uses statistical processes, is used in Lean. It starts with the idea that a product must have value and not just be produced. Lean aims to reduce waste and improve product quality as it is produced.
Problem solving for PDCA
There are some differences between PDCA and DMAIC problem solving, but both are based on the DMAIC approach. The PDCA cycle requires more planning and analysis. PDCA is not as effective as DMAIC for urgent problems. This approach requires a problem-solving leader with technical skills. Six Sigma is looking for a problem-solving partner who is certified as a Six Sigma green belt practitioner.
In Six Sigma, problem-solving follows a cycle that was first introduced in the 1950s by W. Edwards Deming. It was created to be used in combination with continuous improvement methods to rebuild Japan's industrial sectors. The P (Plan) stage requires real data to be gathered and a clear mission. After the PDCA, the team should decide on a suggested solution.

Process maps
One key difference between Six Sigma processes maps and Lean is the way each describes them. Both emphasize defining a process in detail, but each methodology focuses on different aspects of the process. Lean, on the other hand, is about mapping actual processes rather than standard operating procedures. When creating process maps, consider major activities, decisions, and sources of approval. Include areas that require multiple methods and factors. Carefully match roles and review the process flow.
To illustrate the process flow, a process map must include steps, symbols, or arrows. To ensure accuracy, each process should be reviewed and approved by multiple people. Process maps should contain the date they were created as well as who to contact for questions. Overall, process maps are a good way to improve a process. However, they can be complicated.
Analysis of cause & effect
Six Sigma and lean project management techniques include statistical analysis and stochastic optimizing. The Cause and Effect Matrix is a way to link the steps in a process with their outputs and inputs. The customer's requirements will be listed in the order that they are most important. Inputs, outputs, and their impact on the outcome are ranked. Key process input variables and their ranking should be determined.
Although each technique may have its own set of benefits they are not all the same. Lean Six Sigma uses a process management methodology that is based around Frederick Winslow Taylor’s Principles of Scientific Management. Taylor saw business as interconnected workflows and processes. Taylor advocated reducing variation and also minimizing waste. In the process of reducing waste, Six-Sigma and lean are complementary.
Eliminating variation
Variability is part of every manufacturing process. Variability in manufacturing processes can cause uncertainty regarding the outcome. Consistency is essential to provide professional results. Six Sigma and Lean manufacturing methods are designed to reduce variation. Although some variation is normal, excessive variation can lead to problems, rework, or even worse, business consequences. The best way of dealing with variation is to identify its root causes.
First, look at the decision points to find variations. Process maps, which are represented in diamonds, identify decision points. Six Sigma teams can begin by identifying decision points, and then start eliminating variations. This information comes from the Six Sigma owner. The Six Sigma Team cannot focus on any process that the owner isn't following a standardized process. If the Six Sigma team does not have sufficient technical ability to make adjustments, a process diagram may not be useful.
FAQ
Why automate your warehouse?
Modern warehouses have become more dependent on automation. The rise of e-commerce has led to increased demand for faster delivery times and more efficient processes.
Warehouses have to be flexible to meet changing requirements. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. The benefits of automating warehouses are numerous. Here are some reasons why it's worth investing in automation:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Safety is boosted
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale up more easily
-
This makes workers more productive
-
Gives you visibility into all that is happening in your warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
This reduces downtime while increasing uptime
-
Quality products delivered on time
-
Eliminates human error
-
It ensures compliance with regulations
Can we automate some parts of manufacturing?
Yes! Yes. The Egyptians invent the wheel thousands of year ago. Today, robots assist in the assembly of lines.
There are many applications for robotics in manufacturing today. These include:
-
Line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that produce products
Automation could also be used to improve manufacturing. For instance, 3D printing allows us make custom products and not have to wait for months or even weeks to get them made.
What are the 7 R's of logistics?
The 7R's of Logistics is an acronym for the seven basic principles of logistics management. It was developed and published by the International Association of Business Logisticians in 2004 as part of the "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The following letters make up the acronym:
-
Responsible - ensure that actions are in compliance with legal requirements and do not cause harm to others.
-
Reliable - have confidence in the ability to deliver on commitments made.
-
Use resources effectively and sparingly.
-
Realistic - consider all aspects of operations, including cost-effectiveness and environmental impact.
-
Respectful - show respect and treat others fairly and fairly
-
Reliable - Find ways to save money and increase your productivity.
-
Recognizable is a company that provides customers with value-added solutions.
What is production planning?
Production Planning involves developing a plan for all aspects of the production, including scheduling, budgeting, casting, crew, location, equipment, props, etc. This document aims to ensure that everything is planned and ready when you are ready to shoot. This document should include information about how to achieve the best results on-set. This information includes locations, crew details and equipment requirements.
First, you need to plan what you want to film. You may have decided where to shoot or even specific locations you want to use. Once you have identified your locations and scenes, you can start working out which elements you require for each scene. If you decide you need a car and don't know what model to choose, this could be an example. If this is the case, you might start searching online for car models and then narrow your options by selecting from different makes.
Once you have found the right car, you can start thinking about extras. Do you have people who need to be seated in the front seat? Or perhaps you need someone walking around the back of the car? Maybe you'd like to change the interior from black to a white color. These questions will help you determine the exact look and feel of your car. Another thing you can do is think about what type of shots are desired. Will you be filming close-ups or wide angles? Maybe you want the engine or the steering wheels to be shown. These details will help identify the exact car you wish to film.
Once you have all the information, you are ready to create a plan. The schedule will show you when to begin shooting and when to stop. A schedule for each day will detail when you should arrive at the location and when you need leave. It will help everyone know exactly what they have to do and when. Hire extra staff by booking them ahead of time. It's not worth paying someone to show up if you haven't told him.
It is important to calculate the amount of filming days when you are creating your schedule. Some projects only take one or two days, while others may last weeks. When you are creating your schedule, you should always keep in mind whether you need more than one shot per day or not. Multiple takes at the same place will result in higher costs and longer completion times. It is better to be cautious and take fewer shots than you risk losing money if you are not sure if multiple takes are necessary.
Budgeting is another important aspect of production planning. As it will allow you and your team to work within your financial means, setting a realistic budget is crucial. If you have to reduce your budget due to unexpected circumstances, you can always lower it later. However, you shouldn't overestimate the amount of money you will spend. You'll end up with less money after paying for other things if the cost is underestimated.
Production planning is a complicated process. But once you understand how everything works together, it becomes much easier to plan future project.
What does it take to run a logistics business?
A successful logistics business requires a lot more than just knowledge. You must have good communication skills to interact effectively with your clients and suppliers. You must be able analyze data and draw out conclusions. You will need to be able handle pressure well and work in stressful situations. In order to innovate and create new ways to improve efficiency, creativity is essential. You must be a strong leader to motivate others and direct them to achieve organizational goals.
You should also be organized and efficient to meet tight deadlines.
What do you mean by warehouse?
Warehouses and storage facilities are where goods are kept before being sold. It can be indoors or out. It may also be an indoor space or an outdoor area.
Statistics
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma and Manufacturing
Six Sigma can be described as "the use of statistical process control (SPC), techniques to achieve continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department created Six Sigma at their Tokyo plant, Japan in 1986. Six Sigma's core idea is to improve the quality of processes by standardizing and eliminating defects. In recent years, many companies have adopted this method because they believe there is no such thing as perfect products or services. Six Sigma's main objective is to reduce variations from the production average. You can calculate the percentage of deviation from the norm by taking a sample of your product and comparing it to the average. If the deviation is excessive, it's likely that something needs to be fixed.
Understanding the dynamics of variability within your business is the first step in Six Sigma. Once you have a good understanding of the basics, you can identify potential sources of variation. This will allow you to decide if these variations are random and systematic. Random variations happen when people make errors; systematic variations are caused externally. If you make widgets and some of them end up on the assembly line, then those are considered random variations. But if you notice that every widget you make falls apart at the exact same place each time, this would indicate that there is a problem.
Once you've identified where the problems lie, you'll want to design solutions to eliminate those problems. You might need to change the way you work or completely redesign the process. After implementing the new changes, you should test them again to see if they worked. If they don't work, you will need to go back to the drawing boards and create a new plan.